|
|
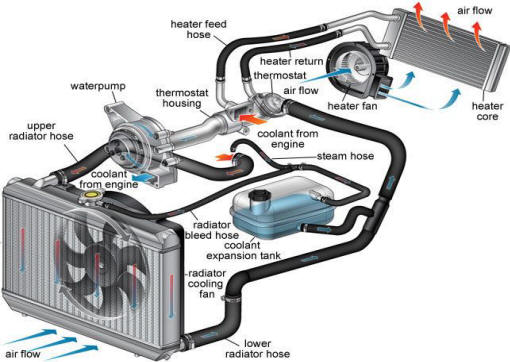
Cooling System
The cooling system's function is to maintain an
efficient engine operating temperature during all
engine speeds and operating conditions. The cooling
system is designed to remove approximately one-third
of the heat produced by the burning of the air-fuel
mixture. When the engine is cold, the system cools
slowly or not at all. This allows the engine to warm
quickly.
Panerai Replica Watches
Cooling Cycle
Coolant is drawn from the radiator outlet and into
the water pump inlet by the water pump. Some coolant
will then be pumped from the water pump, to the
heater core, then back to the water pump. This
provides the passenger compartment with heat and
defrost.
Coolant is also pumped through the water pump outlet
and into the engine block. In the engine block, the
coolant circulates through the water jackets
surrounding the cylinders where it absorbs heat.
The coolant is then forced through the cylinder head
gasket openings and into the cylinder heads. In the
cylinder heads, the coolant flows through the water
jackets surrounding the combustion chambers and
valve seats, where it absorbs additional heat.
From the cylinder heads, the coolant is then forced
to the thermostat. The flow of coolant will either
be stopped at the thermostat until the engine is
warmed or it will flow through the thermostat and
into the radiator where it is cooled and the coolant
cycle is completed.
Operation of the cooling system requires proper
functioning of all cooling system components. The
cooling system consists of the following components:
Audemars Piguet Replica
Coolant
The engine coolant is a solution made up of a 50-50
mixture of Antifreeze
and clean drinkable water. The coolant solution
carries excess heat away from the engine to the
radiator, where the heat is dissipated to the
atmosphere.

Radiator
The radiator is a heat exchanger. The radiator
removes heat from the coolant passing through it.
The fins on the core absorb heat from the coolant
passing through the tubes. As air passes between the
fins, it absorbs heat and cools the coolant.

Pressure Cap
The pressure cap is a cap that seals and pressurizes
the cooling system. It contains a blow off or
pressure valve and a vacuum or atmospheric valve.
The pressure valve is held against its seat by a
spring of predetermined strength, which protects the
radiator by relieving pressure if it exceeds 15 psi.
The vacuum valve is held against its seat by a
spring, which permits opening of the valve to
relieve vacuum created in the cooling system as it
cools off. The vacuum, if not relieved, might cause
the radiator to collapse.

Coolant Recovery System
The coolant recovery system consists of a plastic
coolant recovery reservoir and overflow tube. The
recovery reservoir is also called a recovery tank or
expansion tank. It is partially filled with coolant
and is connected to the radiator fill neck with the
overflow tube. Coolant can flow back and forth
between the radiator and the reservoir.
In effect, a cooling system with a coolant recovery
reservoir is a closed system. When the pressure in
the cooling system gets too high, it will open the
pressure valve in the pressure cap. This allows the
coolant, which has expanded due to being heated, is
allowed to flow through the overflow tube and into
the recovery reservoir. As the engine cools down,
the temperature of the coolant drops and a vacuum is
created in the cooling system. This vacuum opens the
vacuum valve in the pressure cap, allowing some of
the coolant in the reservoir to be siphoned back
into the radiator. Under normal operating
conditions, no coolant is lost. Although the coolant
level in the recovery reservoir goes up and down,
the radiator and cooling system are kept full. An
advantage to using a coolant recovery reservoir is
that it eliminates almost all air bubbles from the
cooling system. Coolant without bubbles absorbs heat
much better than coolant with bubbles.

Water Pump
The water pump is a centrifugal vane impeller type
pump. The pump consists of a housing with coolant
inlet and outlet passages and an impeller. The
impeller is a flat plate mounted on the pump shaft
with a series of flat or curved blades or vanes.
When the impeller rotates, the coolant between the
vanes is thrown outward by centrifugal force.
The purpose of the water pump is to circulate
coolant throughout the cooling system. The water
pump is driven by the crankshaft via the drive belt.

Thermostat
The thermostat is a coolant flow control component.
It's purpose is to regulate the operating
temperature of the engine.
When the coolant temperature is below 91°C (195°F),
the thermostat valve remains closed. This prevents
circulation of the coolant to the radiator and
allows the engine to warm up quickly. After the
coolant temperature reaches 91°C (195°F), the
thermostat valve will open. The coolant is then
allowed to circulate through the thermostat to the
radiator where the engine heat is dissipated to the
atmosphere.

Following are all part of the engine cooling system:
Coolant
Coolant Hose
Coolant Reservoir
Engine - Coolant Temperature Sensor/Switch
Fan Blade
Fan Shroud
Heater Core
Heater Hose
Radiator
Radiator Cap
Radiator Cooling Fan
Radiator Cooling Fan Control Module
Radiator Cooling Fan Motor
Radiator Cooling Fan Motor Relay
Radiator Hose
Temperature Sensor (Gauge)
Thermostat
Thermostat Bypass Hose
Water Pump
If you are
losing coolant and the car is overheating, let the
engine cool off, when there is no more pressure in
the system, remove the radiator cap and make sure
the radiator is full of coolant. A lot of people
just add water to the coolant recovery tank, that
will not help. If there is a leak, than the system
with not suck the fluid in the tank into the
radiator.
Do not waste your money on Antifreeze if you know
that you are losing coolant. Temporarily adding
water will be fine.
If the car is overheating, chances are air
conditioning system will be blowing warm air too.
Never remove the radiator cap on a hot engine. It
will explode and cause chemical burns.
Do not keep driving an overheating car. The damage
caused to the engine can be very extensive and
expensive to repair. |
|



